使用期限租赁或*
许可形式单机和网络版
原产地美国
介质下载
适用平台window,mac,linux
科学软件网销售软件达19年,有丰富的销售经验以及客户资源,提供的产品涵盖各个学科,包括经管,仿真,地球地理,生物化学,工程科学,排版及网络管理等。此外,我们还提供很多附加服务,如:现场培训、课程、解决方案、咨询服务等。
STATA 新功能
ERM=内生性+选择+处理
在连续、二元、有序和删剪结果中结合内源性变量、样本选择和模型的内源性处理
潜在类别分析(LCA)
发现并理解数据中未被观测到的组。使用LCA基于模型的分类功能找出分组
一共有多少个分组
这些分组中都有谁
这些分组有什么区别
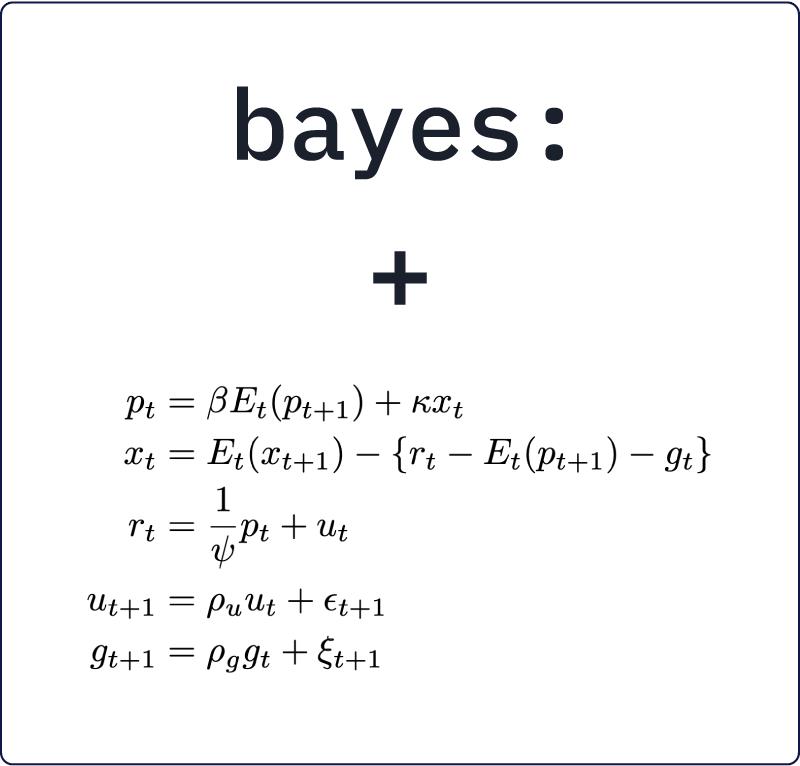
叶斯:logistic和其他44种新功能
输入 bayes:45个Stata评估命令都可以用来拟合贝叶斯回归模型
完整的数据管理功能
Stata的数据管理功能让您控制所有类型的数据。
您可以重组数据,管理变量,并收集各组并重复统计。您可以处理字节,整数,long, float,double和字符串变量(包括BLOB和达到20亿个字符的字符串)。Stata还有一些的工具用来管理的数据,如生存/时间数据、时间序列数据、面板/纵向数据、分类数据、多重替代数据和调查数据。
Stata轻松生成出版质量、风格迥异的图形。您可以编写脚本并以可复制的方式生成成百上千个图形,并且可以以EPS或TIF格式输出打印、以PNG格式或SVG格式输出放到网上、或PDF格式输出预览。使用这个图形编辑器可更改图形的任何方面,或添加标题、注释、横线、箭头和文本。
Frequentist analysis is entirely data-driven and strongly depends on whether or not the data
assumptions required by the model are met. On the other hand, Bayesian analysis provides a more
robust estimation approach by using not only the data at hand but also some existing information or
knowledge about model parameters.
In frequentist statistics, estimators are used to approximate the true values of the unknown parameters,
whereas Bayesian statistics provides an entire distribution of the parameters. In our example of a
prevalence of an infectious disease from What is Bayesian analysis?, frequentist analysis produced one
point estimate for the prevalence, whereas Bayesian analysis estimated the entire posterior distribution
of the prevalence based on a given sample.

Building a reliable Bayesian model requires extensive experience from the researchers, which leads
to the second difficulty in Bayesian analysis—setting up a Bayesian model and performing analysis
is a demanding and involving task. This is true, however, to an extent for any statistical modeling
procedure.
Lastly, one of the main disadvantages of Bayesian analysis is the computational cost. As a rule,
Bayesian analysis involves intractable integrals that can only be computed using intensive numerical
methods. Most of these methods such as MCMC are stochastic by nature and do not comply with
the natural expectation from a user of obtaining deterministic results. Using simulation methods does
not compromise the discussed advantages of Bayesian approach, but unquestionably adds to the
complexity of its application in practice.

Frequentist inference is based on the sampling distributions of estimators of parameters and provides
parameter point estimates and their standard errors as well as confidence intervals. The exact sampling
distributions are rarely known and are often approximated by a large-sample normal distribution.
Bayesian inference is based on the posterior distribution of the parameters and provides summaries of
this distribution including posterior means and their MCMC standard errors (MCSE) as well as credible
intervals. Although exact posterior distributions are known only in a number of cases, general posterior
distributions can be estimated via, for example, Markov chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) sampling without
any large-sample approximation.
Frequentist confidence intervals do not have straightforward probabilistic interpretations as do
Bayesian credible intervals. For example, the interpretation of a 95% confidence interval is that if
we repeat the same experiment many times and compute confidence intervals for each experiment,
then 95% of those intervals will contain the true value of the parameter. For any given confidence
interval, the probability that the true value is in that interval is either zero or one, and we do not
know which. We may only infer that any given confidence interval provides a plausible range for the
true value of the parameter. A 95% Bayesian credible interval, on the other hand, provides a range
for a parameter such that the probability that the parameter lies in that range is 95%.
科学软件网不定期举办各类公益培训和讲座,让您有更多机会免费学习和熟悉软件。
http://turntech8843.b2b168.com








